
Electronic configuration Definition, Orbitals, & Facts Britannica
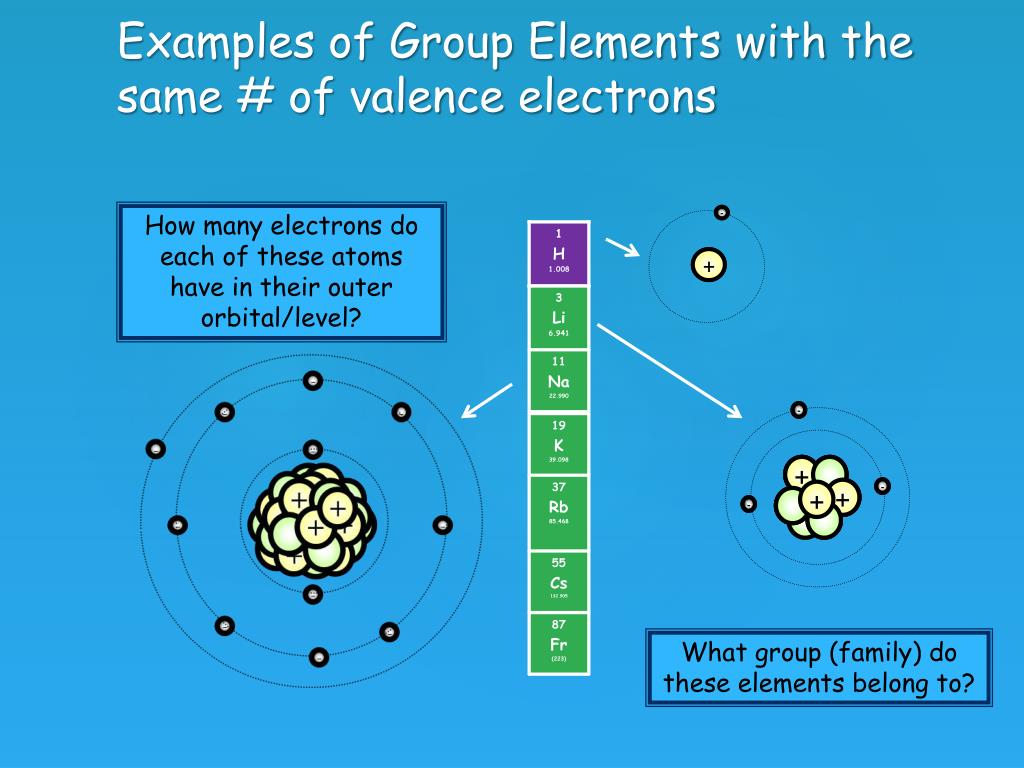
So the full electron configuration is 1S2, 2S2, 2P6, and 3S1. When I want to figure out how many valence electrons sodium has, the number of valence electrons would be equal to the number of electrons in the outermost shell, the outermost energy level. For sodium, sodium has the first energy level, second energy level, and the third energy level.
Elements Their Atomic, Mass Number,Valency And Electronic Configuratio
How many valence electrons does boron have? Recognize that the second principal energy level consists of both the \(2s\) and the \(2p\) sublevels, and so the answer is three. B: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1 (there are three electrons on the highest occupied energy level n=2)
Valence Electrons — Definition & Importance Expii
Determine the total number of valence (outer shell) electrons. The sum of the valence electrons is 5 (from N) + 6 (from O) = 11. The odd number immediately tells us that we have a free radical, so we know that not every atom can have eight electrons in its valence shell. Draw a skeleton structure of the molecule. We can easily draw a skeleton.

free printable periodic table with names charges valence electrons
In this table, you can see that helium has a full valence shell, with two electrons in its first and only, 1n, shell. Similarly, neon has a complete outer 2n shell containing eight electrons.. So Na has one electron in its outermost orbital. Another example that I'll use is Fluorine (F). Its electronic configuration is 1s2, 2s2, 2p5.

What Are Valence Electrons How To Find Valence Electrons
The electron configuration of sodium shows that there is an unpaired electron in the last orbit of sodium. Therefore, the valency of sodium is 1. How many valence electrons does sodium ion(Na +) have? The elements that have 1, 2, or 3 electrons in the last shell donate the electrons in the last shell during bond formation.
PPT Valence Electrons PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5581383
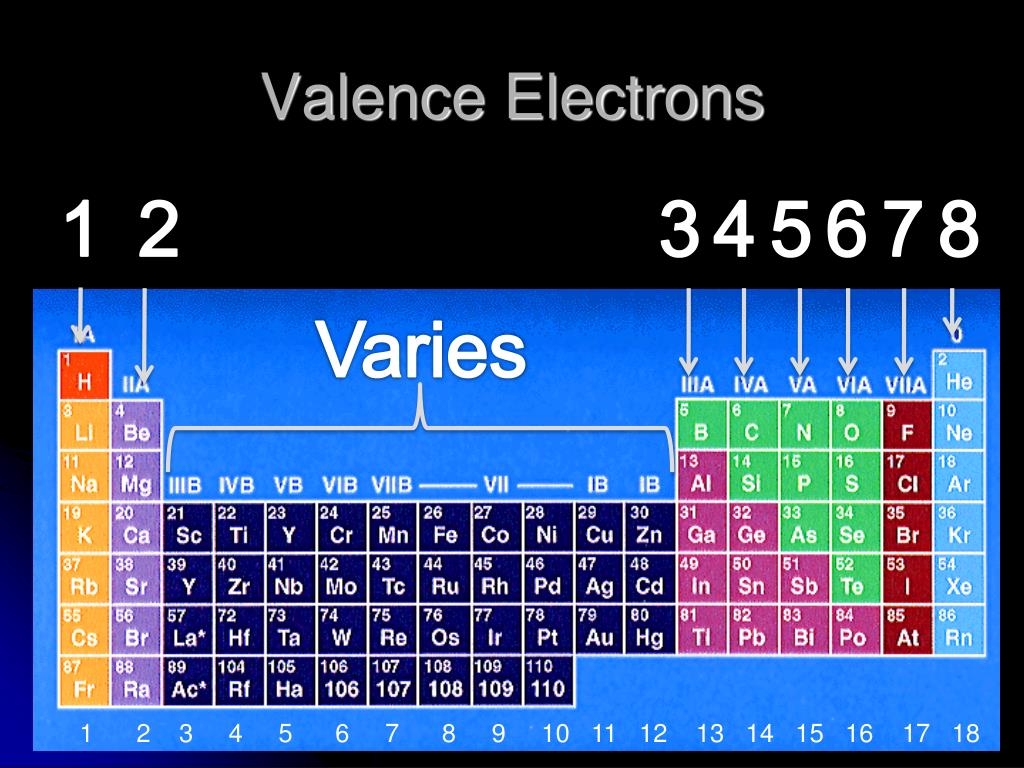
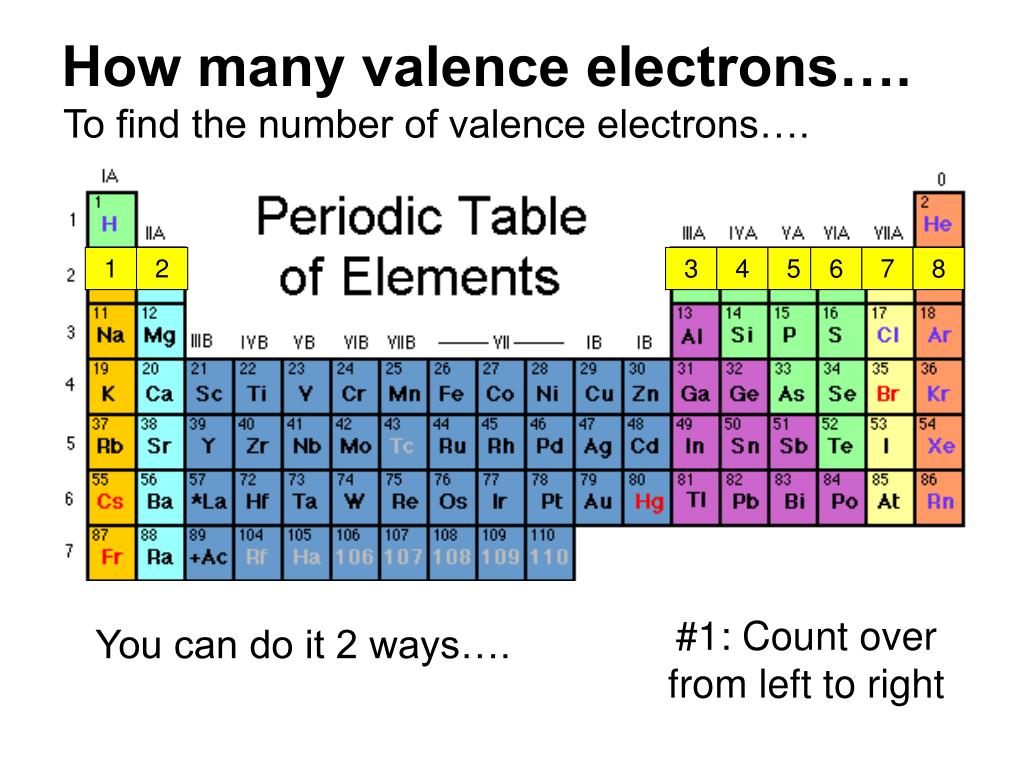
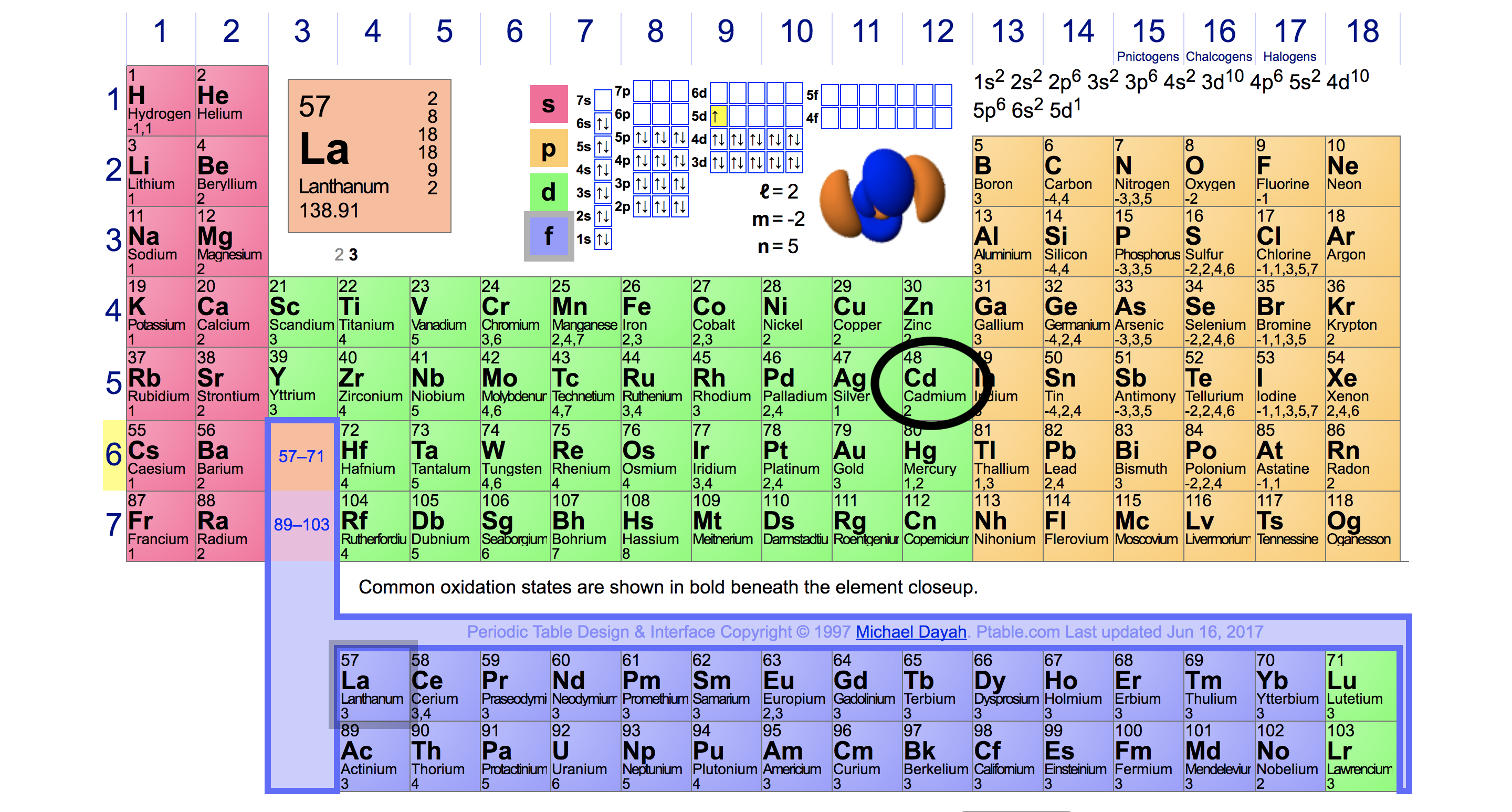
You can easily determine the number of valence electrons an atom can have by looking at its Group in the periodic table. For example, atoms in Groups 1 and 2 have 1 and 2 valence electrons, respectively. Atoms in Groups 13 and 18 have 3 and 8 valence electrons, respectively. Valence electrons are responsible for the reactivity of an element.
PPT Classic Chem PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2464733
Thus, sodium ion (Na+) has eight valence electrons. Na+ valency is not zero like noble gas as their outermost shell has eight electrons. when a sodium atom loses one electron, Na+ ion is produced and that's what valency is. So that Na+ valency is +1 not zero. Chemical Properties Sodium (Na) atom. Atomic number: 11:

How to find Valency? What are valence electrons? Teachoo (2023)
To facilitate our understanding of how valence electrons interact, a simple way of representing those valence electrons would be useful. A Lewis electron dot symbol (or electron dot diagram or a Lewis diagram or a Lewis structure) is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number.

Sodium Valence Electrons Sodium Valency (Na) with Dot Diagram
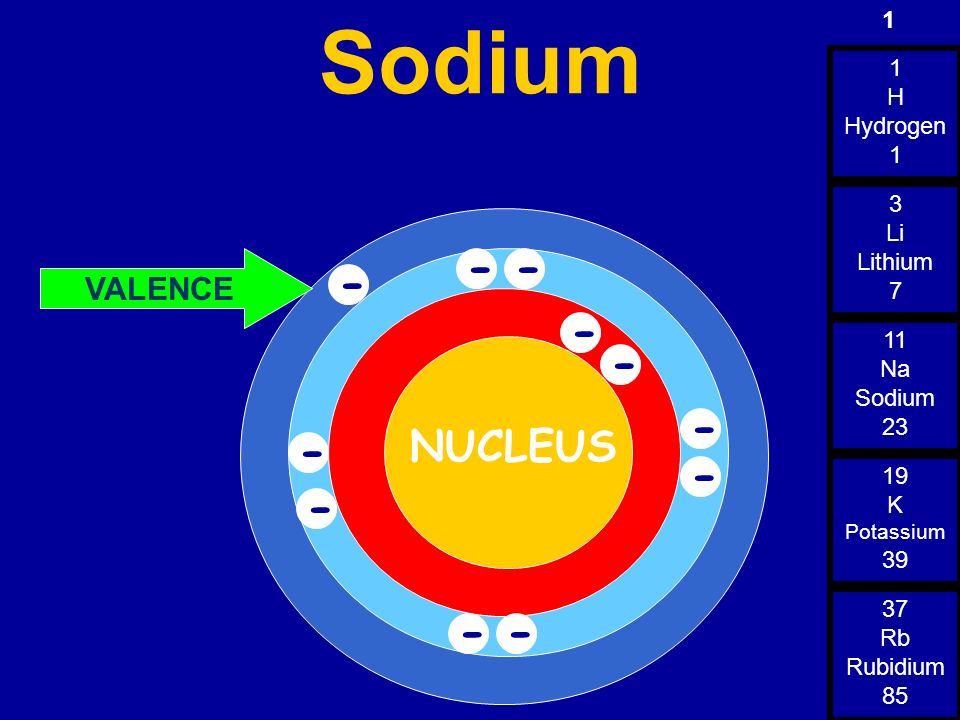
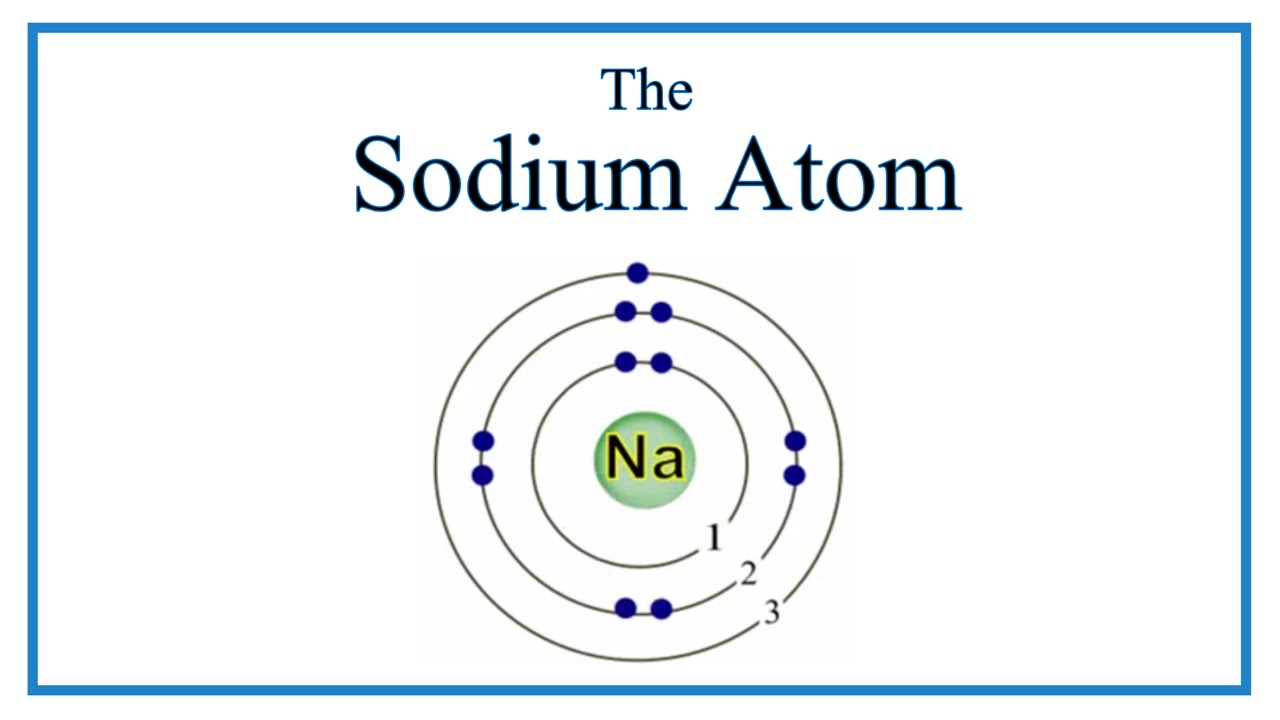
So, sodium's 11 electrons are arranged this way: 2 electrons in the first "shell", 8 electrons in the second "shell"; and 1 electron (the valence electron) in the third "shell". We write this as 2.8.1. The last number is how we know the number of valence electrons. Aluminium has the electron arrangement 2.8.3. It has 3 valence electrons.

Electron Dot Diagram Periodic Table
For example, silicon is in Group IVA (Group 14), so each atom would have four valence electrons. Chlorine is in Group VIIA (Group 17), so it would have seven valence electrons. Calcium would have two valence electrons, since it is in Group IIA (Group 2). Helium is the only exception for the main group elements. The first energy level holds a.

Sodium Na (Element 11) of Periodic Table NewtonDesk
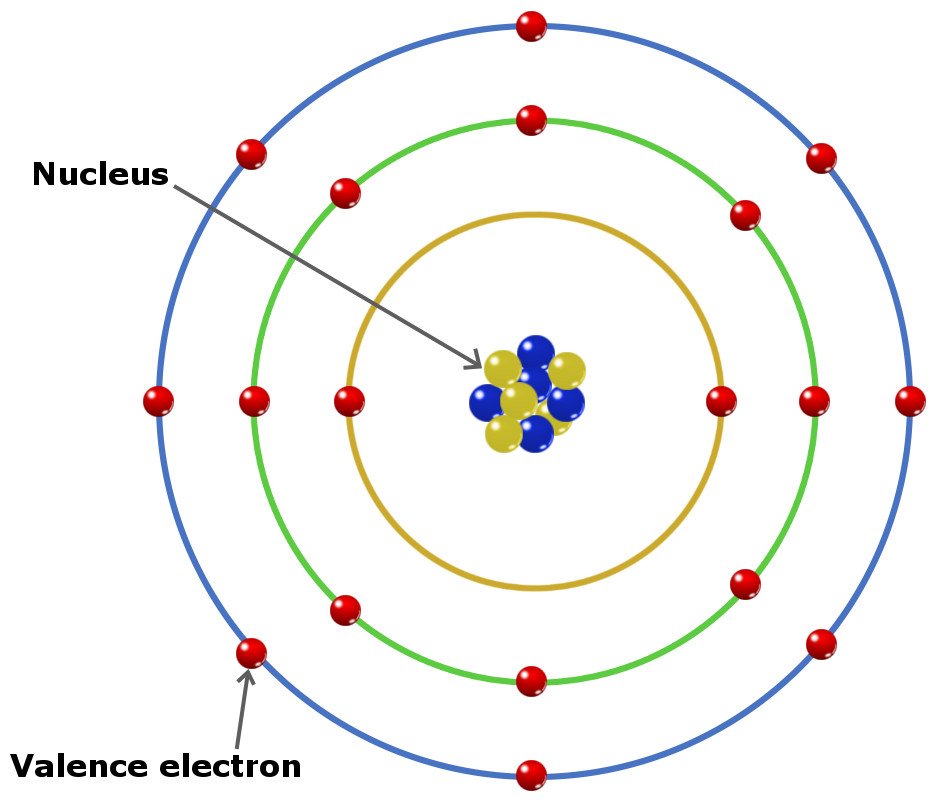
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell, or energy level, of an atom. For example, oxygen has six valence electrons, two in the 2s subshell and four in the 2p subshell. We can write the configuration of oxygen's valence electrons as 2s²2p⁴. Created by Sal Khan.
How Many Valence Electrons Does Titanium Have rjhinteriordesigndenver
Sodium, with a total of 11 electrons, has only one electron in its third and outermost shell. Because the outermost shell comes into direct contact with other atoms when a chemical reaction takes place, the valence electrons play a big role in determining the chemical reactivity of an element and the elements with which it will react to form.
Periodic table of elements with valence electrons kcJuli
Referring to the octet rule, atoms attempt to get a noble gas electron configuration, which is eight valence electrons. Sodium has one valence electron, so giving it up would result in the same electron configuration as neon. Chlorine has seven valence electrons, so if it takes one it will have eight (an octet)..
Valency of Sodium How many valence electrons does Sodium (Na) have?
For groups 13 to 18, subtract 10 from the group number to get the number of valence electrons, e.g., elements from group 13 will have three valence electrons, from group 14 four valence electrons, and so on. A notable case is group 18, in which the elements (known as noble gases) have 8 valence electrons.
Sodium Diagram
This table of element valences includes the maximum valence and most common valence values. Use this is a reference with a periodic table.. so don't always assume an element's valence is determined by the number of electrons in its outer shell. Table of Element Valences. Number : Element. Sodium +1: 12: Magnesium +2: 13: Aluminum +3: 14.
Lead Periodic Table Protons Neutrons And Electrons Matttroy
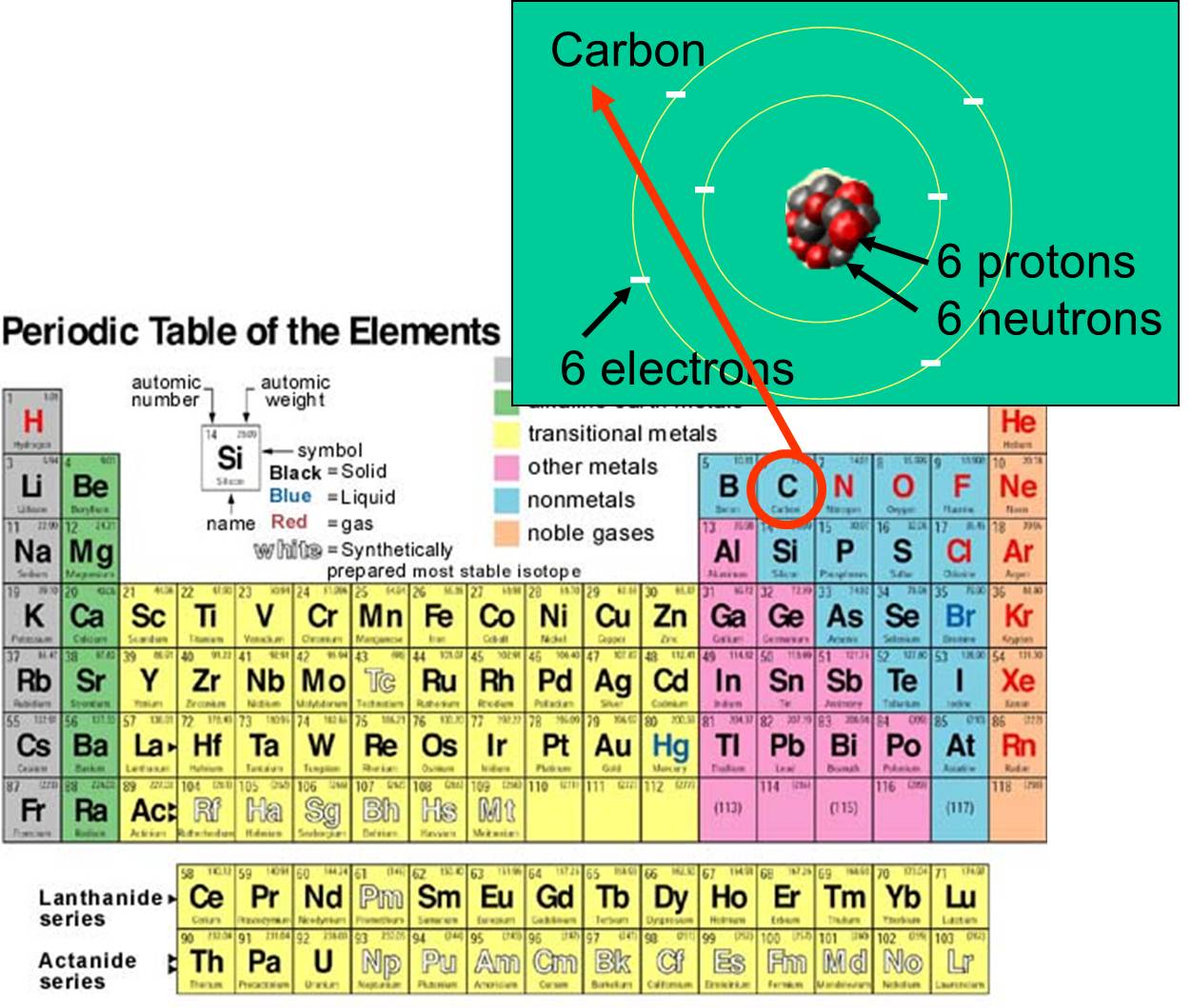
Four covalent bonds.Carbon has four valence electrons and here a valence of four. Each hydrogen atom has one valence electron and is univalent. In chemistry and physics, valence electrons are electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond if the outermost shell is not closed. In a single covalent bond, a shared pair forms with both.